Dear NHS England Patients & Information Directorate,
We’ve been very patient patients in the care.data pause. Please can we have some answers now?
I would like to call for greater transparency and openness about the promises made to the public, project processes & policies and your care.data communication plans.
In 2013, in the Health Service Journal Mr. Kelsey wrote:
“When patients are ignored, they are most at risk; that was the central conclusion of the report by Robert Francis into Stafford hospital.
Don Berwick, in his safety review, said the NHS should be “engaging, empowering and hearing patients and their carers all the time.
“That has been my mission since I started as National Director for Patients and Information: to support health and care services transform transparency and participation.“
HSJ, 10th December 2013
It is time to walk-the-talk for care.data under this banner of transparency, participation and open government.
Response to the Listening exercises
The care.data listening phase, introduced by the pause announced on February 18th, has captured a mass of questions, the majority of which still remain unaddressed.
At one of these sessions, [the 1-hr session on June 17th Open House, linking ca. 100 people at each of the locations in Basingstoke, Leicester, London, and York] participants were promised that our feedback would be shared with us later in the summer, and posted online. After the NHS AGM on Sept 18th I was told it would happen ‘soon’. It is still not in the public domain.
At every meeting all the unanswered questions, on post-it notes, in table-group minutes or scribbled flipcharts, were gathered ‘to be answered at a later date’. When will that be?
To date, there has been no published information which addresses the unanswered event questions.
Transparency of Process, Policies and Approach
The care.data Programme Board has held meetings to plan the rollout process, policies and approach. The minutes and materials from which have not been published. I find this astonishing when one considers that the minutes of the care.data advisory group, NIB (new), CAG, GPES advisory or even NHS England Board itself are in the public domain. I believe the care.data Programme Board meeting materials should be too.
It was acknowledged through the Partridge Review of past use of our hospital records that this HES data is not anonymous. The extent of its sale to commercial third-parties and use by police and the Home Office was revealed. This is our medical data we gave to hospitals and in our wider medical use for our care. Why are we the last to hear it’s being accessed by all sorts of people who are not at all involved in our clinical care?
Even for commissioning purposes it is unclear how these datasharing reasons are justified when the Caldicott Review said extracting identifiable data for risk stratification or commissioning could not be assumed under some sort of ‘consent deal’?
The 251 approval just got extended *again* – until 30th April 2015. If you can’t legally extract data without repeat approvals from on high, then maybe it’s time to question why?
The DoH, NHS England Patients and Information Directorate, HSCIC, and indeed many data recipients, all appear to have normalised an approach that for many is still a shock. The state centralised and passed on our medical records to others without our knowledge or permission. For years. With financial exchange.
Amazingly, it continues to be released in this way today, still without our consent or fair processing or publicised way to opt out.
“To earn the public’s trust in future we must be able to show that our controls are meticulous, fool-proof and solid as a rock.” said Sir Nick Partridge in his summary review.
Now you ask us to trust in care.data that the GP data, a degree more personal, will be used properly.
Yet you ask us to do this without significant changes in legislation to safeguard tightly defined purposes who can access it and why, how we control what future changes may be made without our knowledge and without a legally guaranteed opt out.
There is no information about what social care dataset is to be included in future, so how can we know what care.data scope even is yet?
Transparency cannot be a convenient watch word which applies with caveats. Quid pro quo, you want our data under an assumed consent process, then guarantee a genuinely informed public.
You can’t tell patients one approach now, then plan to change what will be said after the pilot is complete, knowingly planning a wider scope to include musculoskeletal or social care data and more. Or knowing you plan to broaden users of data [like research and health intelligence currently under discussion at IAG ] but only communicate a smaller version in the pilot. That is like cheating on a diet. You can’t say and do one thing in public, then have your cake and eat it later when no one is looking. It still counts.
In these processes, policies and approach, I don’t feel my trust can be won back with lack of openness and transparency. I don’t yet see a system which is, ‘meticulous, fool-proof or solid as a rock’.
‘Pathfinder’ pilots
Most recently you have announced that four areas of CCGs will pilot the ‘pathfinder’ stage in the rollout of phase one. But where and when remains a mystery. Pathfinder communications methods may vary from place to place and trial what works and what fails. One commendable method will be a written letter.
However even given that individual notice intent, we cannot ignore that many remaining questions will be hard to address in a leaflet or letter. They certainly won’t fit into an SMS text.
Why pilot communications at all which will leave the same open questions unanswered you already know, but have not answered?
For example, let’s get a few of the missing processes clarified up front:
- How will you communicate with Gillick competent children, whose records may contain information about which their parents are not aware?
- How will you manage this for elderly or vulnerable patients in care homes and with diminished awareness or responsibility?
- What of the vulnerable at risk of domestic abuse and coercion?
- When things change in scope or use, how will we be given the choice to change our opt out decision?
I ask you not to ignore the processes which remain open. They need addressed BEFORE the pilot, unless you want people to opt out on the basis of their uncertainty and confusion.
What you do now, will set the model expectations for future communications. Patient online. Personalised medicine. If NHS health and social care is to become all about the individual, will you address all individuals equally or is reaching some less important than others?
It seems there is time and effort in talking to other professionals about big data, but not to us, whose data it is. Dear Patients & Information Directorate, you need to be talking to us, before to others about how to use us.
In March, this twelve point plan made some sensible suggestions.
Many of them remain unaddressed. You could start there. But in addition it must be clear before getting into communications tools, what is it that the pathfinders are actually piloting?
You can’t pilot communications without clearly defined contents to talk about.
Questions of substance need answers, the ten below to start with.
What determines that patients understand the programme and are genuinely informed, and how will it be measured?
Is it assumed that pilots will proceed to extraction? Or will the fair processing efforts be evaluated first and the effort vs cost be taken into account whether it is worth proceeding at all?
Given the cost involved, and legal data protection requirements, surely the latter? But the pathfinder action plan conflates the two.
Citizen engagement
Let’s see this as an opportunity to get care.data right, for us, the patients. After all, you and the rest of the NHS England Board were keen to tell us at the NHS AGM on September 18th, how valuable citizen engagement is, and to affirm that the NHS belongs to us all.
How valued is our engagement in reality, if it is ignored? How will involvement continue to be promoted in NHS Citizen and other platforms, if it is seen to be ineffective? How might this negatively affect future programmes and our willingness to get involved in clinical research if we don’t trust this basic programme today?
This is too important to get wrong. It confuses people and causes concern. It put trust and confidence in jeopardy. Not just for now, but for other future projects. care.data risks polluting across data borders, even to beyond health:
“The care.data story is a warning for us all. It is far better if the industry can be early on writing standards and protocols to protect privacy now rather than later on down the track,” he said. [David Willets, on 5G]
So please, don’t keep the feedback and this information to internal departments.
We are told it is vital to the future of our NHS. It’s our personal information. And both belong to us.
During one Health Select Committee hearing, Mr. Kelsey claimed: “If 90 per cent opt out [of care.data], we won’t have an NHS.”
The BMA ARM voted in June for an opt in model.
ICO has ruled that an opt in model by default at practice level with due procedures for patient notification will satisfy both legal requirements and protect GPs in their role as custodians of confidentiality and data controllers. Patient Concern has called for GPs to follow that local choice opt in model.
I want to understand why he feels what the risk is, to the NHS and examine its evidence base. It’s our NHS and if it is going to fail without care.data and the Board let it come to this, then we must ask why. And we can together do something to fix it. There was a list of pre-conditions he stated at those meetings would be needed before any launch, which the public is yet to see met. Answering this question should be part of that.
It can’t afford to fail, but how do we measure at what cost?
I was one of many, including much more importantly the GPES Advisory Group, who flagged the shortcomings of the patient leaflet in October 2013, which failed to be a worthwhile communications process in January. I flagged it with comms teams, my MP, the DoH.
[Sept 2013 GPES Advisory] “The Group also had major concerns about the process for making most patients aware of the contents of the leaflets before data extraction for care.data commenced”.
No one listened. No action was taken. It went ahead as planned. It cost public money, and more importantly, public trust.
In the words of Lord Darzi,
“With more adroit handling, this is a row that might have been avoided.”
Now there is still a chance to listen and to act. This programme can’t afford to pilot another mistake. I’m sure you know this, but it would appear that with the CCG announcement, the intent is to proceed to pilot soon. Ready or not.
If the programme is so vital to the NHS future, then let’s stop and get it right. If it’s not going to get the participation levels needed, then is it worth the cost? What are the risks and benefits of pressing ahead or at what point do we call a halt? Would it be wise to focus first on improving the quality and correct procedures around the data you already have – before increasing the volume of data you think you need? Where is the added intelligence, in adding just more information?
Is there any due diligence, a cost benefit analysis for care.data?
Suggestions
Scrap the ‘soon’ timetable. But tell us how long you need.
The complete raw feedback from all these care.data events should be made public, to ensure all the questions and concerns are debated and answers found BEFORE any pilot.
The care.data programme board minutes papers and all the planning and due diligence should be published and open to scrutiny, as any other project spending public funds should be.
A public plan of how the pathfinders fit into the big picture and timeline of future changes and content would remove the lingering uncertainty of the public and GPs: what is going on and when will I be affected?
The NHS 5 year forward view was quite clear; our purse strings have been pulled tight. The NHS belongs to all of us. And so we should say, care.data can’t proceed at any and at all costs. It needs to be ‘meticulous, fool-proof and solid as a rock’.
We’ve been patient patients. We should now expect the respect and response, that deserves.
Thank you for your consideration.
Yours sincerely.
Addendum: Sample of ten significant questions still outstanding
1. Scope: What is care.data? Scope content is shifting. and requests for scope purposes are changing already, from commissioning only to now include research and health intelligence. How will we patients know what we sign up to today, stays the purposes to which data may be used tomorrow?
2. Scope changes fair processing: We cannot sign up to one thing today, and find it has become something else entirely tomorrow without our knowledge. How will we be notified of any changes in what is to be extracted or change in how what has been extracted is to be used in future – a change notification plan?
3. Purposes clarity: Who will use which parts of our medical data for what? a: Clinical care vs secondary uses:
Given the widespread confusion – demonstrated on radio and in press after the pathfinders’ announcement – between care.data which is for ‘secondary use’ only, i.e. purposes other than the direct care of the patient – and the Summary Care Record (SCR) for direct care in medical settings, how will uses be made very clear to patients and how it will affect our existing consent settings?
3. Purposes definition: Who will use which parts of our medical data for what? b) Commercial use It is claimed the Care Act will rule out “solely commercial”purposes, but how when what remains is a broad definition open to interpretation? Will “the promotion of health” still permit uses such as marketing? Will HSCIC give its own interpretation, it is after all, the fact it operates within the law which prescribes what it should promote and permit.
3. Purposes exclusion: Who will use which parts of our medical data for what? c) Commercial re-use by third parties: When will the new contracts and agreements be in place? Drafts on the HSCIC website still appear to permit commercial re-use and make no mention of changes or revoking licenses for intermediaries.
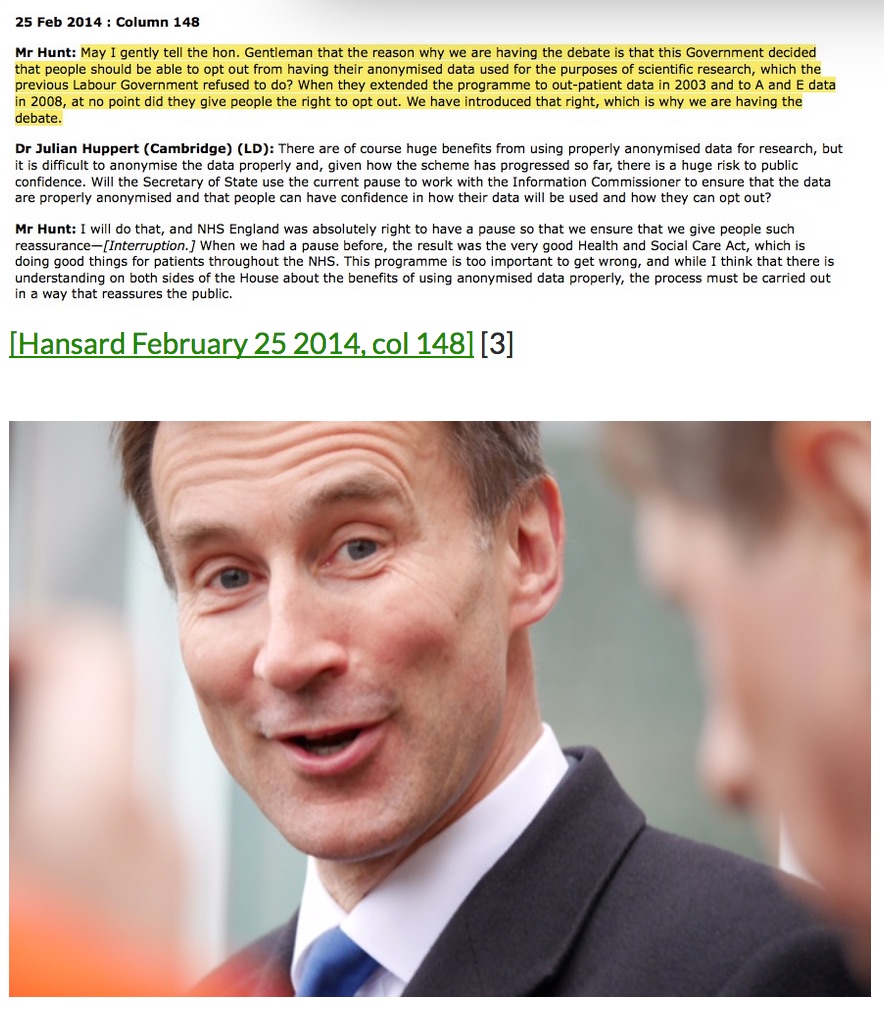
4a. Opt out: It is said that patients who opt out will have this choice respected by the Health and Social Care Information Centre (i.e. no data will be extracted from their GP record) according to the Secretary of State for Health [col 147] – but when will the opt out – currently no more than a spoken promise – be put on a statutory basis? There seem to be no plans whatsoever for this.
Further wider consents: how patients will know what they have opted into or out from is currently almost impossible. We have the Summary Care Record, Proactive care in some local areas, different clinical GP systems, the Electronic Prescription Service and soon to be Patient Online, all using different opt in methods of asking and maintaining data and consent, means patients are unsurprisingly confused.
4b. Opt out: At what point do you determine that levels of participation are worth the investment and of value? If parts of the population are not represented, how will it be taken into account and remain valuable to have some data? What will be statistically significant?
5. Legislation around security: The Care Act 2014 is supposed to bring in new legislation for our data protection. But there are no changes to date as far as I can see – what happened to the much discussed in Parliament, one strike and out. Is any change still planned? If so, how has this been finalised and with what wording, will it be open to Parliamentary scrutiny? The Government claim to have added legal protection is meaningless until the new Care Act Regulations are put in front of Parliament and agreed.
6. What of the Governance changes discussed?
There was some additional governance and oversight promised, but to date no public communication of changes to the data management groups through the HRA CAG or DAAG and no sight of the patient involvement promised.
The Data Guardian role remains without the legal weight that the importance of its position should command. It has been said this will be granted ‘at the earliest opportunity.’ Many seem to have come and gone.
7. Data security: The planned secure data facility (‘safe setting’) at HSCIC to hold linked GP and hospital data is not yet built for expanded volume of data and users expected according to Ciaran Devane at the 6th September event. When will it be ready for the scale of care.data?
Systems and processes on this scale need security designed, that scales up to match in size with the data and its use.
Will you proceed with a pilot which uses a different facility and procedures from the future plan? Or worse still, with extracting data into a setting you know is less secure than it should be?
8. Future content sharing: Where will NHS patients’ individual-level data go in the longer term? The current documentation says ‘in wave 1’ or phase one, which would indicate a future change is left open, and indicated identifiable ‘red’ data is to be shared in future? “care.data will provide the longer term visions as well as […] the replacement for SUS.”
9. Current communications:
- How will GPs and patients in ‘pathfinder’ practices be contacted?
- Will every patient be written to directly with a consent form?
- What will patients who opted out earlier this year be told if things have changed since then?
- How will NHS England contact those who have retired or moved abroad recently or temporarily, still with active GP records?
- How will foreign pupils’ parents be informed abroad and rights respected?
- How does opt out work for sealed envelopes?
- All the minorities with language needs or accessibility needs – how will you cater for foreign language, dialect or disability?
- The homeless, the nomadic, children-in-care
- How can we separate these uses clearly from clinical care in the public’s mind to achieve a genuinely informed opinion?
- How will genuine mistakes in records be deleted – wrong data on wrong record, especially if we only get Patient Online access second and then spot mistakes?
- How long will data be retained for so that it is relevant and not excessive – Data Protection principle 3?
- How will the communications cater for both GP records and HES plus other data collection and sharing?
- If the plan is to have opt out effective for all secondary uses, communications must cater for new babies to give parents an informed choice from Day One. How and when will this begin?
No wonder you wanted first no opt out, then an assumed consent via opt out junk mail leaflet. This is hard stuff to do well. Harder still, how will you measure effectiveness of what you may have missed?
10. Pathfinder fixes: Since NHS England doesn’t know what will be effective communications tools, what principles will be followed to correct any failures in communications for any particular trial run and how will that be measured?
How will patients be asked if they heard about it and how will any survey, or follow up ensure the right segmentation does not miss measuring the hard to reach groups – precisely those who may have been missed? i.e. If you only inform 10% of the population, then ask that same 10% if they heard of care.data, you would expect a close to 100% yes. That’s not reflective that the whole population was well informed about the programme.
If it is shown to have been ineffective, at what point do you say Fair Processing failed and you cannot legally proceed to extraction?
> This list doesn’t yet touch on the hundreds of questions generated from public events, on post-its and minutes. But it would be a start.
*******
References for remaining questions:
17th June Open House: Q&A
17th June Open House: Unanswered public Questions
Twelve point plan [March 2014] positive suggestions by Jeremy Taylor, National Voices
6th September care.data meeting in London
image quote: Winnie The Pooh, A.A. Milne