This Valentine’s I was thinking about the restructuring of education in England and its wide ranging effects. It’s all about the break up.
The US EdTech market is very keen to break into the UK, and our front door is open.
We have adopted the model of Teach First partnered with Teach America, while some worry we do not ask “What is education for?”
Now we hear the next chair of Oftsed is to be sought from the US, someone who is renowned as “the scourge of the unions.”
Should we wonder how long until the management of schools themselves is US-sourced?
The education system in England has been broken up in recent years into manageable parcels – for private organisations, schools within schools, charity arms of commercial companies, and multi-school chains to take over – in effect, recent governments have made reforms that have dismantled state education as I knew it.
Just as the future vision of education outlined in the 2005 Direct Democracy co-authored by Michael Gove said, “The first thing to do is to make existing state schools genuinely independent of the state.”
Free schools touted as giving parents the ultimate in choice, are in effect another way to nod approval to the outsourcing of the state, into private hands, and into big chains. Despite seeing the model fail spectacularly abroad, the government seems set on the same here.
Academies, the route that finagles private corporations into running public-education is the preferred model, says Mr Cameron. While there are no plans to force schools to become academies, the legislation currently in ping-pong under the theme of coasting schools enables just that. The Secretary of State can impose academisation. Albeit only on Ofsted labeled ‘failing’ schools.
What fails appears sometimes to be a school that staff and parents cannot understand as anything less than good, but small. While small can be what parents want, small pupil-teacher ratios, mean higher pupil-per teacher costs. But the direction of growth is towards ‘big’ is better’.
“There are now 87 primary schools with more than 800 pupils, up from 77 in 2014 and 58 in 2013. The number of infants in classes above the limit of 30 pupils has increased again – with 100,800 pupils in these over-sized classes, an increase of 8% compared with 2014.” [BBC]
All this restructuring creates costs about which the Department wants to be less than transparent. And has lost track of.
If only we could see that these new structures raised standards? But,” while some chains have clearly raised attainment, others achieve worse outcomes creating huge disparities within the academy sector.”
If not delivering better results for children, then what is the goal?
A Valentine’s view of Public Service Delivery: the Big Break up
Breaking up the State system, once perhaps unthinkable is possible through the creation of ‘acceptable’ public-private partnerships (as opposed to outright privatisation per se). Schools become academies through a range of providers and different pathways, at least to start with, and as they fail, the most successful become the market leaders in an oligopoly. Ultimately perhaps, this could become a near monopoly. Delivering ‘better’. Perhaps a new model, a new beginning, a new provider offering salvation from the flood of ‘failing’ schools coming to the State’s rescue.
In order to achieve this entry to the market by outsiders, you must first remove conditions seen as restrictive, giving more ‘freedom’ to providers; to cut corners make efficiency savings on things like food standards, required curriculum, and numbers of staff, or their pay.
And what if, as a result, staff leave, or are hard to recruit?
Convincing people that “tech” and “digital” will deliver cash savings and teach required skills through educational machine learning is key if staff costs are to be reduced, which in times of austerity and if all else has been cut, is the only budget left to slash.
Self-taught systems’ providers are convincing in their arguments that tech is the solution.
Sadly I remember when a similar thing was tried on paper. My first year of GCSE maths aged 13-14 was ‘taught’ at our secondary comp by working through booklets in a series that we self-selected from the workbench in the classroom. Then we picked up the master marking-copy once done. Many of the boys didn’t need long to work out the first step was an unnecessary waste of time. The teacher had no role in the classroom. We were bored to bits. By the final week at end of the year they sellotaped the teacher to his chair.
I kid you not.
Teachers are so much more than knowledge transfer tools, and yet by some today seem to be considered replaceable by technology.
The US is ahead of us in this model, which has grown hand-in-hand with commercialism in schools. Many parents are unhappy.
So is the DfE setting us up for future heartbreak if it wants us to go down the US route of more MOOCs, more tech, and less funding and fewer staff? Where’s the cost benefit risk analysis and transparency?
We risk losing the best of what is human from the classroom, if we will remove the values they model and inspire. Unions and teachers and educationalists are I am sure, more than aware of all these cumulative changes. However the wider public seems little engaged.
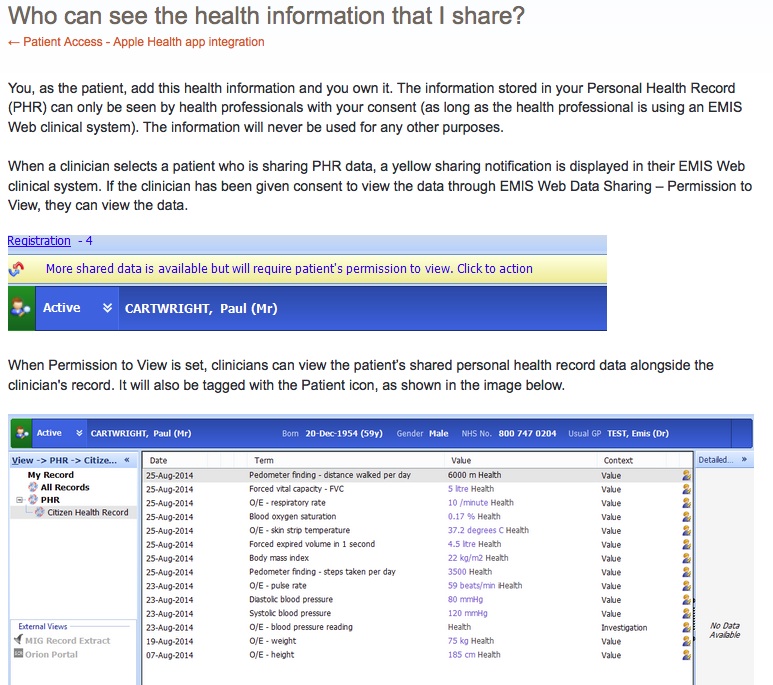
For anyone ‘in education’ these changes will all be self-evident and their balance of risks and benefits a matter of experience, and political persuasion. As a parent I’ve only come to understand these changes, through researching how our pupils’ personal and school data have been commercialised, given away from the National Pupil Database without our consent, since legislation changed in 2013; and the Higher Education student and staff data sold.
Will more legislative change be needed to keep our private data accessible in public services operating in an increasingly privately-run delivery model? And who will oversee that?
The Education Market is sometimes referred to as ‘The Wild West’. Is it getting a sheriff?
The news that the next chair of Oftsed is to be sought from the US did set alarm bells ringing for some in the press, who fear US standards and US-led organisations in British schools.
“The scourge of unions” means not supportive of staff-based power and in health our junior doctors have clocked exactly what breaking their ‘union’ bargaining power is all about. So who is driving all this change in education today?
Some ed providers might be seen as profiting individuals from the State break up. Some were accused of ‘questionable practices‘. Oversight has been lacking others said. Margaret Hodge in 2014 was reported to have said: “It is just wrong to hand money to a company in which you have a financial interest if you are a trustee.”
I wonder if she has an opinion on a lead non-executive board member at the Department for Education also being the director of one of the biggest school chains? Or the ex Minister now employed by the same chain? Or that his campaign was funded by the same Director? Why this register of interests is not transparent is a wonder.
It could appear to an outsider that the private-public revolving door is well oiled with sweetheart deals.
Are the reforms begun by Mr Gove simply to be executed until their end goal, whatever that may be, through Nikky Morgan or she driving her own new policies?
If Ofsted were to become US-experience led, will the Wild West be tamed or US providers invited to join the action, reshaping a new frontier? What is the end game?
Breaking up is not hard to do, but in whose best interest is it?
We need only look to health to see the similar pattern.
The structures are freed up, and boundaries opened up (if you make the other criteria) in the name of ‘choice’. The organisational barriers to break up are removed in the name of ‘direct accountability’. And enabling plans through more ‘business intelligence’ gathered from data sharing, well, those plans abound.
Done well, new efficient systems and structures might bring public benefits, the right technology can certainly bring great things, but have we first understood what made the old less efficient if indeed it was and where are those baselines to look back on?
Where is the transparency of the end goal and what’s the price the Department is prepared to pay in order to reach it?
Is reform in education, transparent in its ideology and how its success is being measured if not by improved attainment?
The results of change can also be damaging. In health we see failing systems and staff shortages and their knock-on effects into patient care. In schools, these failures damage children’s start in life, it’s not just a ‘system’.
Can we assess if and how these reforms are changing the right things for the right reasons? Where is the transparency of what problems we are trying to solve, to assess what solutions work?
How is change impact for good and bad being measured, with what values embedded, with what oversight, and with whose best interests at its heart?
2005’s Direct Democracy could be read as a blueprint for co-author Mr Gove’s education reforms less than a decade later.
Debate over the restructuring of education and its marketisation seems to have bypassed most of us in the public, in a way health has not.
Underperformance as measured by new and often hard to discern criteria, means takeover at unprecedented pace.
And what does this mean for our most vulnerable children? SEN children are not required to be offered places by academies. The 2005 plans co-authored by Mr Gove also included: “killing the government’s inclusion policy stone dead,” without an alternative.
Is this the direction of travel our teachers and society supports?
What happens when breakups happen and relationship goals fail?
Who picks up the pieces? I fear the state is paying heavily for the break up deals, investing heavily in new relationships, and yet will pay again for failure. And so will our teaching staff, and children.
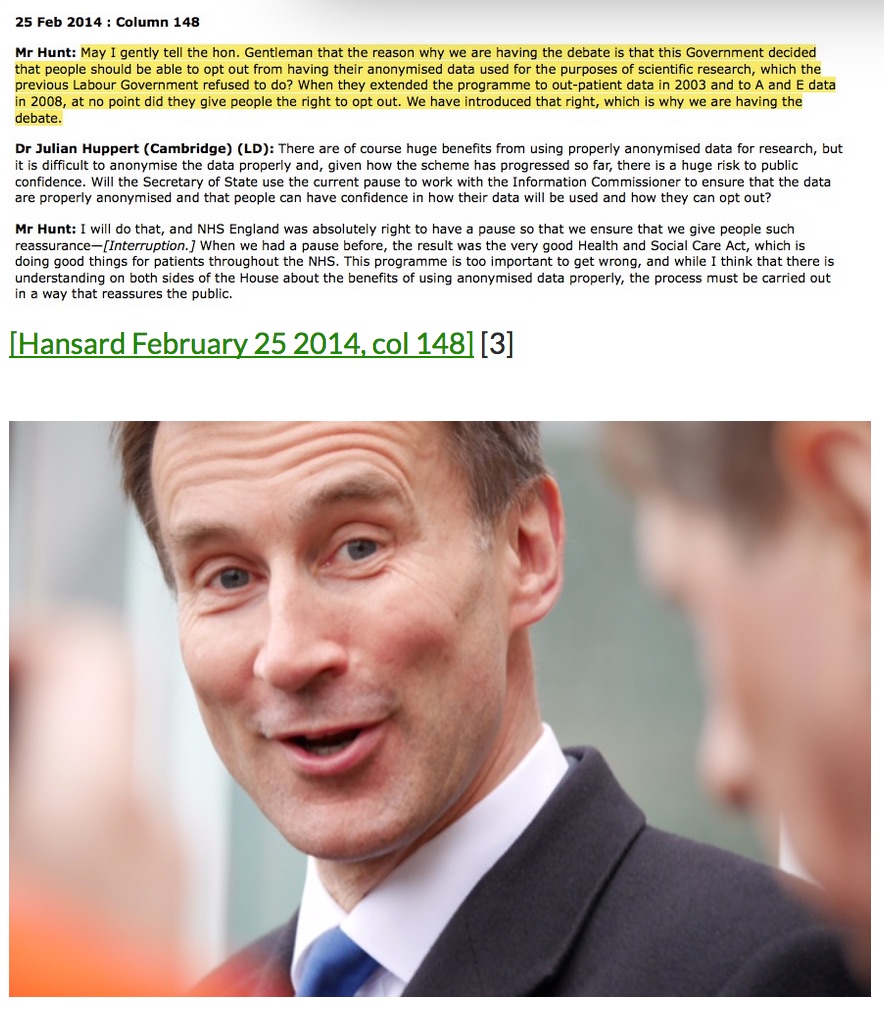
While Mr Hunt is taking all the heat right now, for his part in writing Direct Democracy and its proposals to privatise health – set against the current health reforms and restructuring of junior doctors contracts – we should perhaps also look to Mr Gove co-author, and ask to better understand the current impact of his recent education reforms, compare them with what he proposed in 2005, and prepare for the expected outcomes of change before it happens (see p74).
One outcome was that failure was to be encouraged in this new system, and Sweden held up as an exemplary model:
“Liberating state schools would also allow the all-important freedom to fail.”
As Anita Kettunen, principal of JB Akersberga in Sweden reportedly said when the free schools chain funded by a private equity firm failed:
“if you’re going to have a system where you have a market, you have to be ready for this.”
Breaking up can be hard to do. Failure hurts. Are we ready for this?
******
Abbreviated on Feb 18th.