Eleven months ago, care.data was put on hold and promises made to listen to professional and public opinion, which would shape programme improvement.
Today, Sir Bruce Keogh of NHS England said: “an unprecedented shift of resources and care into GP surgeries was necessary to help the NHS withstand the twin pressures of rising demand and tight budgets.”
[The Guardian, 19 Jan 2015]
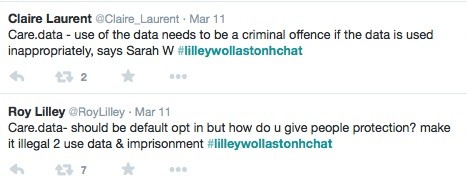
care.data right now, seems like the straw on the camel’s back that GPs do not need, and that in its current format, many patients do not want.
Why the rush to get it implemented and will the costs of doing so, – to patients, to professionals and to the programme – be worth it?
What has NHS England heard from these listening events?
The high level ‘you said, we did’ document, sharing some of the public concerns raised with care.data, has been published by NHS England.
It is an aggregated, high level presentation, but I wonder if it really offers much more insight than everyone knew a year ago? It’s a good start, but does it suggest any real changes have taken place as a result of listening and public feedback?
Where are we now, what does it tell us, and how will it help?
Some in the media argue, like this article, that a:
“massive privacy campaign effectively put a halt to it last year.”
In reality it was the combination of the flaws in the care.data plans for the GP data extraction and sharing programme, and past NHS data sharing practices, which was its own downfall.
Campaigners merely pointed these flaws out.
Once they were more apparant, many bodies involved in good data sharing and those with concerns for confidentiality, came together with suggestions to make improvements.
But to date and a year after patients first became aware of the issues, even this collaboration has not yet solved patients’ greatest concern, that data is being given, without the individuals’ knowledge or consent, to third parties for non-clinical care, without oversight once they receive it.
The HSCIC 2013-15 Roadmap outlined HSCIC would ‘agree a plan for addressing the barriers to entry into the market for new commercial ventures’ using our data provided by the HSCIC and:
“Help stimulate the market through dynamic relationships with commercial organisations, especially those who expect to use its data and outputs to design new information-based services.”
Working with care.data was first promised,
to ‘innovators of all kinds’ just as HES was delivered to commercial businesses, [including reportedly
Google, and PA Consulting getting 15 years of NHS data], all with unclear and unproven patient benefit or UK plc economic development and gain.
Patients are concerned about this.
They have asked about the assurance given that the purposes are more defined but still don’t rule out commercial users, re-use licences have not been categorically ruled out, and patients have asked further, detailed questions, which are still open.
View some of them for yourself here: including coercion, disability inclusion, and time and time again concerns over the accuracy and quality of records, which may be uploaded, and mistakes never deleted upon which judgments are made, from records which the patient may never have seen.
care.data events have been hosted by and held for a group of charities, other care.data listening events held by the care.data advisory group, [include Peterborough and Coin Street, London] [you can view the 26th November Manchester event with questions from 33 minutes in] and those held as part of the NHS Open House event in June [from 01:13.06 in the NHS Open House video], all asked sensible detailed questions on process and practice which are still to be addressed, which are not in the high level ‘you said, we did.’
Technical and practical processes of oversight have been changed to improve the way in which data was shared, but what about data use that has been the crux of patient concern?
How will the questions that remain unanswered be addressed? – because it seems the patient letter, posters and flyers won’t do it.
What now?
Communications are rolling out in pathfinders
All year the message has been the same: communication was poor.
“We have heard, loud and clear, that we need to be clearer about the care.data programme and that we need to provide more support to GPs to communicate the benefits and the risks of data sharing with their patients, including their right to opt out.” [October 2014, Mr. Kelsey, NHS England]
The IIGOP report on care.data outlined in December 2014 what still remains to be done and the measures required for a success.
These go far beyond communications issues.
But if pathfinders are being asked to spend time and money now, it must be analysed now, what will new communications materials look like, compared with those from a year ago.
Whilst I would agree that communications were poor, the question that remains to be asked is why? Why was communication poor? Why did a leaflet that was criticised by ICO, criticised by the GPES advisory group, criticised by many more and glaringly a failed piece of communication to outsiders, why was all that advice and criticism ignored and it got sent [or not sent] to patients across England?
[Sept 2013 GPES Advisory] “The Group also had major concerns about the process for making most patients aware of the contents of the leaflets before data extraction for care.data commenced”.
We could say it doesn’t matter. However it is indicative of the same issues now, as then, and throughout the year. There has been lots of positive advice given, shared, and asked for at patient listening events. If this is the extent of “you said, we did”, feedback is still being ignored. That matters.
Because if it continues to be, any new communications will have the same failure-to-launch that they did a year ago.
In the last year we have heard repeatedly, that the pause will enable the reshaping of communications materials.
Sadly, the bell hasn’t rung yet, on what really needs done. It looks to me as though the communications people have done their best, dealing with glaring gaps in content.
Communications materials are not ready, because it’s not clear where care.data is going, or what’s the point of the trip.

All change?
It has failed to address the programme as a change issue.
That is what it is at its core, and it is this failure which explains why it has met so much resistance.
If the 26th November Manchester questions are anything to go by the reason for the change as to why our data is needed at all, remains very unclear, for professionals and patients.
How patients will be empowered to manage its ongoing changes into the future, is also undefined.
In addition, there has been little obvious, measurable change in the substance of the programme communication in the last 12 months.
New materials suggest no real changes have taken place as a direct result of listening to public feedback at all. They may have from feedback that was given before the pause, but what impact has the pause had?
If you disagree, look over the GP care.data leaflet from 2013 and see what changes you would make now. Look at the 2013 patient leaflet and see what substantial improvement there is. Look at the basic principles of data protection and see if the care.data programme communications clearly and simply address them any better now.
What are the new plans for new communications, and how do they pick up on the feedback given at ‘hundreds’ of listening events?
The communications documents are a good start at addressing a complex set of questions.
However, whilst they probably meet their spec it doesn’t meet their stated objective: to show clear ‘we did’ nor a clear future action plan.
The listening feedback may have been absorbed, but hasn’t generated any meaningful new communications output.
It shows as far as listening goes, real communications in this one-way format, may have reached the end of the line.
How can patients make a decision on an unknown?
The new communications in posters and the ‘you said, we did’, state that access to the information collected will be limited in the pathfinder – but it does not address the question in the longer term.
This is a key question for patients.
It should be simple. Who will have access to my data and why?
No caveats, no doubts, no lack of clarity.
Patients should be properly informed how ALL their data is being used that is held by HSCIC. The opt out talked in February 2014 of two options; for data to be extracted under care.data at GPs and all the other data already stored at the HSCIC from hospitals and elsewhere. To explain those two different options patients first need told about all the data which is stored, and how it is used.
Talk about the linkage with other datasets, the future extraction and use of social care data, the access given via the back office to police and other non-health government departments. Stop using ‘your name will not be used’ in materials like the original patient leaflet – It may be factual for care.data per se, but is misleading on what of our personal data is extracted and used without our consent or awareness – most of us don’t know the PDS extracts name at all.
Being cagey does not build trust. Incomplete explanation of uses would surely not meet the ICO data protection requirements of fair processing either. And future uses remain unexplained.
For care.data this is the unknown.
NHS England is yet to publish any defined future use and scope change process, though its plan is clearly mapped:
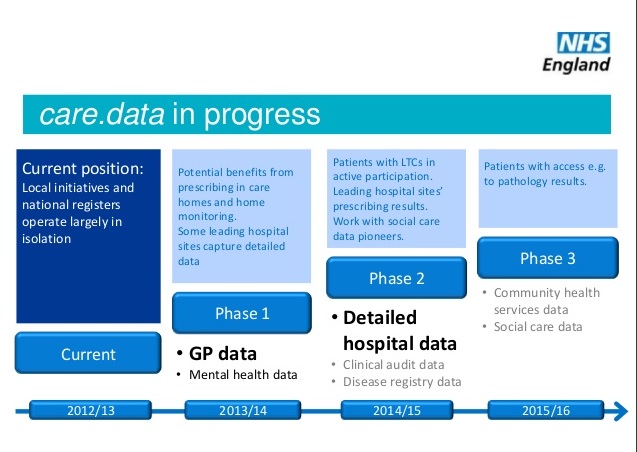
There must be a process of how to notify patients either of what will be extracted, or who will be given access to use it > a change process. A basic building block for fair processing. Not a back door.
It needs to address: how is a change identified, who will be notified within what time frame before the extraction, how will the training and access changes be given, and how will patients be informed of the change in what may be extracted or who may be using it and be given the right to change their opt in / out selection. The law requires fair processing BEFORE the change happens.
We patients should also be made aware what impact this choice has on data already extracted, and that nothing will be deleted from our history. Even if its clearly a mistake. How does that affect reports?
Communication is impossible whilst the content & scope is moving.
I’ve been banging on, quite frankly, about scope, since March.
This is what needs done. Pull over, and get the fixes done.
> Don’t roll out any comms in a pathfinder yet. They’re not ready.
> First sort out the remaining substance so you know what it is that materials are communicating. What, who, why, when, how?
The IIGOP report lists clearly all that needs done and how to measure their success: it’s not communications, it’s content.
The final technical, security and purposes pieces still need resolved; practical questions on opt out, legislation needed to make sure the opt out really is robust, that the so-called ‘one strike and out’ isn’t just a verbal assurance but actually happens, and that future access is defined beyond the pathfinder – who will have access at and outside the new secure lab – not only for the pilot, but future.
Get the definition of scope limited so as to meet fair processing, and get the future scope change communication process ironed out.
How will patients be communicated to not only now, not in a pathfinder, but for every change that happens in the future which has a fair processing requirement?
Only then can the programme start to truly address change and communications with meaningful messages. Until then, it’s PR.
Once you know what you’re saying, how to say it becomes easy.
If it’s not proving easy to do well, we need to ask why.
 >>>References>>>
>>>References>>>
1. You said, we did NHS England presentation
2. IIGOP report into care.data
3. Pharmacists to access DWP data – example of scope change who accesses data and why, which fails fair processing without a change process in place to communicate
>>>>>>>>>
For anyone interested in considering the current materials in detail, see below: this doesn’t address the posters shared in the Manchester event or what is missing, but many of the messages are the same as in the ‘you said, we did’ and it’s a start.
>>>>>>>>>
Addendum:
1. The “co-production” approach to materials
2. Why a scope change management process is vital to trust for care.data.
3. Some feedback on the high level ‘you said, we did’ document
4. What do communications require to improve from those before?
5. Hard questions
1. The “co-production” approach to materials
The IIGOP report on care.data outlined in December 2014 asked a very sound question on page 8:
“What are the implications of using locally developed communications material (“co-production”) for subsequent national rollout ?”
The Programme is developing a “co-production” approach to initial GP and patient-facing material, based on feedback from the care.data “listening period” and from local events and formal research.
“The intent is to ensure that there is local ownership of material used to communicate with professionals and patients in the Pathfinder stage.”
To ask a basic tenet of change management: what’s in it for them?
It’s unclear to what level of detail the national materials will go, and how much local sites will create.
If I were at CCG or GP level and responsible for ‘local ownership’ of communications from this national programme, I’d be asking myself why I am expected to reinvent the wheel? I’d want to use national standards as far as possible.
Why should local organisations have to produce or design materials which should be communicating the intent of a programme whose purpose is to be identical for every one of the 62 million in England registered with a GP? Let’s hope the materials are national.
What benefit will a local level site see, by designing their own materials – it will cost time and money – where’s the benefit for the patients in each practice, for the GPs and the programme?
Is it too cynical to ask, has NHS England not got the resources to do this well and deliver ready-done?
If so, I should urge a rethink at national level, because in terms of time and people’s effort this multiple duplication will be a costly alternative.
It also runs the risk of costly mistakes in accuracy and inconsistency.
There appears to date to be no plan yet how future changes will be communicated. This must be addressed before the pathfinder and in any current communication, and all local sites need the same answer because the new decisions on extraction, will be at national level.
page 9: “present the benefits” – this fails to do so – this is however not a failing of this presentation – there is simply still no adequate cost benefit document available in the public domain.
page 11: “keep data safe” – the secure lab is mentioned – a great forwards step compared with HES access – and it states analysts will only access it there in the pathfinder – but what about after that?
page 13: “explain the opt out clearly”: “You can opt out at any time. Just talk to your GP Practice.” > I have, but as far as I know my data is still released by the HSCIC from HES and wider secondary collections of data, which I did not know were extracted and did not consent to being used for secondary purposes. Opt out doesn’t appear to actually work. Please let me know if that’s a misunderstanding on my part. I’d be delighted to hear it is functional.
page 15: “legislative changes” – the biggest concern patients raise over and over again, is sharing data beyond their direct care with commercial companies and for non-NHS purposes. This has not been excluded. No way round that. No matter how you word it and made harder by the fact that data was released from HES in July to Experian for use in mosaic. If that makes the definition, then it’s loose.
The one-strike-and-out is not mentioned in materials, although it was discussed on Nov 26th in Manchester. When is the legislation to actually happen?
Both this and the opt out are still not on a robust legal basis – much verbal assurance has been given on “legislative changes” but they are meaningless if not enacted.
page 17: “access safeguards” – the new audit trail is an excellent step. But doesn’t help patients know if OUR data was used, it’s generic. We need some sort of personal audit trail of our consent, and show how it is respected in what data is released, to who, when, and why. The over emphasis of ‘only with legal access’ is overdone as 251 has been used to approve data access for years without patient knowledge or consent. If it is to be reassuring, it is somewhat misleading; data is shared much more widely than patients know. If it is to answer questions asked in the listening feedback events, there needs to be an explanation of how the loop will be closed to feed the information back and how it will be of concrete benefit.
And in general:
Either “this will not affect the care you receive” or it will. Both sentences cannot be true. Either way, there should be no coercion of participation:
“If you decide to opt out it won’t affect the care and treatment you receive. However, if significant amounts of people do opt out, we won’t be able to collect enough information to help us improve NHS services across the nation.”
Agreement must in usual medical environments, be given voluntarily and freely, without pressure or undue influence being exerted on the person either to accept or refuse.
3. What do communications require to improve from those before?
a. Lessons Learned for improvement:
The point of the pause was in order to facilitate the changes and improvement needed in the programme, whose flaws were the reason to stop in February. All the questions need shared so that all the CCGs can benefit from all the learning. If all the flaws are not discussed openly, how can they be fixed? Not only being fixed, but being seen to be fixed would be productive and useful for the programme. [The IIGOP report on care.data outlined in December 2014 covers these.]
b. Consistency:
Raw feedback will be vital for CCGs and GP practices to have. It has not been released and the ‘you said, we did’ is a very high level aggregate of what was clear last February. Since then, the detailed questions are what should be given to give all involved the information to able to understand, and to have the answers for consistently.
This way they will be properly prepared for the questions they may get in any pilot rollout. If questions have already been asked in one place, the exact same answer should be reproduced in another.
c. Time-saving:
If the same question has already been asked at a national or regional event, why make the local level search for the same answer again? This could be costly and pointless multiplied many times over.
d. Accuracy:
Communications aren’t always delivered correctly. They can be open to misinterpretation or that the comms team simply gets facts wrong. That would fail data protection requirements and fail to protect GPs. How will this accuracy be measured if done at local level and how will it be measured and by whom?
The IIGOP report asked: “What are the success criteria for the Pathfinders? How will we know what has worked and what has not? “
I know from my own experience that either the communications team or consultants can misunderstand the facts, or something can easily become lost in translation, from the technical theory to the tangible explanation.
4. Future change: Control of scope change for linkage and access
Current communications may address the current pathfinder extraction, but they are not fit for purpose for a rollout which is intended to be long term and ever changing.
So what exactly is it piloting? – a “mini” approach? – if so, to what purpose? or is it just hoping to get X amount of data in, done and dusted, as ‘a start.’
If the pathfinder patients are only told a sub-set of information in a pilot rollout, we should ask:
a. why? Is this in order to make the idea sound more appealing?
b. how will it be ensured that their consent, or lack of objection, is fully informed and therefore meets Data Protection requirements?
and finally
c. how will future changes be communicated? This must be addressed before the pathfinder and in any current communication.
For example; who gets access to data may change so you can’t say only “” access to the information collected will only be given to a limited number of approved analysts who will have to travel to a new secure data facility that the HSCIC is setting up.”
Pharmacists who have access to this data for direct care, may also now be getting access to DWP data.
“the Royal Pharmaceutical Society has already said that the new measures could affect trust between patients and pharmacists.” [EHI Dec 30th 2014]
When patients signed up for the SCR at a GP practice they may not realise it is shared with pharmacies. When data is shared with the Department of Work and Pensions, citizens may not realise it could be shared with pharmacies. Neither told the other when signing up that future access would allow this cross referencing and additional access.
This is a real life scenario that should not be glossed over in a brochure. A hoped for ‘quick-fix’ now, will simply cause later problems, and if data is used inappropriately, there may not be another opportunity for winning back trust again.
To get it legally wrong now, would be inexcusable.
Here’s why it would be better to do no more communications now:
5. Hard questions can’t be avoided
Currently, comms still avoid the hard questions, and those are the ones people want answers for. Open questions remain unaddressed.
Raw questions asked in July at a charities’ event are, with some post-event reshaping and responses here. Note how many are unknowns.
Changes have been suggested to be constructive.
One attendee of a public listening event commented online in October 2014, on the NHS England CCG announcement:
“I am one of those that has tried hard to engage with you to try and make sure that people can be assured that their personal and private information will not be exploited, I feel that you have already made the decision to press ahead regardless and feel very let down.
“Please publish the findings of your listening exercise and tell people how you intend to respond to their concerns before proceeding with this.”
People have engaged and want to be involved in making this programme work better, if it has to work at all like this.
Q: Where is the simple, clear public business case for cost and benefits?
The actual raw questions have been kept unpublished for no clear purpose. It could look like avoiding answering the hard questions.
The IIGOP report captures many of them; for example on process of competence, capacity and processes – and the report shows there is still a need to “demonstrate that what goes on ‘under the bonnet’ of Pathfinder practice systems operates in the same way that patients are being told it does.”
When is the promised legislative change to actually happen? The opt out is still not on a robust legal basis – much verbal assurance has been given on “legislative changes” but they are meaningless if not enacted.
It’s all about trust and that relationship, like the communication and feedback responses, has to be two-way.

![The Economic Value of Data vs the Public Good? [3] The value of public voice.](https://jenpersson.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Trust-e1426443553441-672x372.jpg)


![Wearables: patients will ‘essentially manage their data as they wish’. What will this mean for diagnostics, treatment and research and why should we care? [#NHSWDP 3]](https://jenpersson.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/FullSizeRender1-672x372.jpg)
![smartphones: the single most important health treatment & diagnostic tool at our disposal [#NHSWDP 2]](https://jenpersson.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/IMG_4563-e1427130930127-672x372.jpg)
![Thoughts on Digital Participation and Health Literacy: Opportunities for engaging citizens in the NHS [#NHSWDP 1]](https://jenpersson.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/FullSizeRender-640x372.jpg)