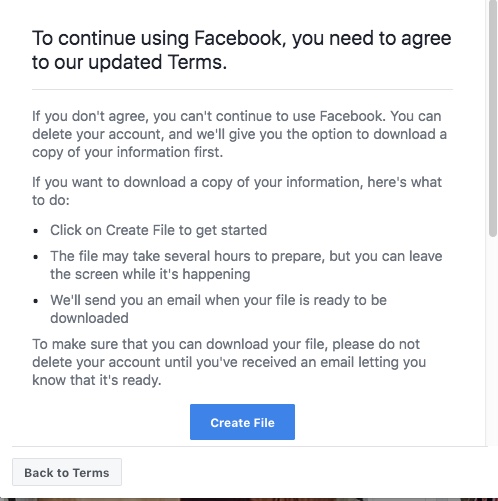
This Facebook ad was the final straw for me this week.
I’m finally leaving.
When I saw Facebook’s disingenuous appropriation of new data law as-a-good-thing I decided time’s up. While Zuckerberg talks about giving users more control, what they are doing is steering users away from better privacy and putting users outside the reach of new protections rather than stepping up to meet its obligations.
After eleven years, I’m done. I’ve used Facebook to run a business. I’ve used it to keep in touch with real-life family and friends. I’ve had more positive than negative experiences on the site. But I’ve packed in my personal account.
I hadn’t actively used it since 2015. My final post that year was about Acxiom’s data broker agreement with Facebook. It has taken 3 hours to download any remaining data, to review and remove others’ tags, posts and shared content linking me. I had already deactivated 18 apps, and have now used each individual ID that the Facebook-App link provided, to make Subject Access requests (SAR) and object to processing. Some were easy. Some weren’t.
Pinterest and Hootsuite were painful circular loops of online ‘support’ that didn’t offer any easy way to contact them. But to their credit Hootsuite Twitter message support was ultra fast and suggested an email to hootsuite-dpa [at] hootsuite.com. Amazon required a log in to the Amazon account. Apple’s Aperture goes into a huge general page impossible to find any easy link to contact. Ditto Networked Blogs.
Another app that has no name offered a link direct to a pre-filled form with no contact details and no option for free text you can send only the message please delete any data you hold about me — not make a SAR.
Another has a policy but no Data Controller listed. Who is http://a.pgtb.me/privacy ? Ideas welcome.
What about our personal data rights?
The Facebook ad says, you will be able to access, download or delete your data at any time. Not according to the definition of personal data we won’t. And Facebook knows it. As Facebook’s new terms and condition says, some things that you do on Facebook aren’t stored in your account. For example, a friend may have messages from you after deletion. They don’t even mention data inferred. This information remains after you delete your account. It’s not ‘your’ data because it belongs to the poster, it seems according to Facebook. But it’s ‘your’ data because the data are about or related to you according to data protection law.
Rights are not about ownership.
That’s what Facebook appears to want to fail to understand. Or perhaps wants the reader to fail to understand. Subject Access requests should reveal this kind of data, and we all have a right to know what the Facebook user interface limits-by-design. But Facebook still keeps this hidden, while saying we have control.
Meanwhile, what is it doing? Facebook appears to be running scared and removing recourse to better rights.
Facebook, GDPR and flaws in Face Recognition
They’ve also started running Face Recognition. With the new feature enabled, you’re notified if you appear in a photo even if not tagged.
How will we be notified if we’re not tagged? Presumably Facebook uses previously stored facial images that were tagged, and is matching them using an image library behind the scenes.
In the past I have been mildly annoyed when friends who should know me better, have posted photos of my children on Facebook.
Moments like children’s birthday parties can mean a photo posted of ten fun-filled faces in which ten parents are tagged. Until everyone knew I’d rather they didn’t, I was often tagged in photos of my young children. Or rather my children were tagged as me.
Depending on your settings, you’ll receive a notification when someone tags a photo with your name. Sure I can go and untag it, to change the audience that can see it, but cannot have control over it.
Facebook meanwhile pushes this back as if it is a flaw with the user and in a classic victim-blaming move suggests it’s your fault you don’t like it, not their failure to meet privacy-by-design, by saying, If you don’t like something you’re tagged in, you can remove the tag or ask the person who tagged you to remove the post.
There is an illusion of control being given to the user, by companies and government at the moment. We must not let that illusion become the accepted norm.
Children whose parents are not on the site cannot get notifications. A parent may have no Facebook account. (A child under 13 should no Facebook account, although Facebook has tried to grab those too.) The child with no account may never know, but Facebook is certainly processing, and might be building up a shadow profile about, the nameless child with face X anyway.
What happens next?
As GDPR requires a share of accountability for controller and processing responsibilities, what will it mean for posters who do so without consent of the people in photos? For Facebook it should mean they cannot process using biometric profiling, and its significant effects may be hidden or, especially for children, only appear in the future.
Does Facebook process across photos held on other platforms?
Since it was founded, Facebook has taken over several social media companies, the most familiar of which are Instagram in 2012 and WhatsApp in 2014. Facebook has also bought Oculus VR [VR headsets], Ascenta [drones], and ProtoGeo Oy [fitness trackers].
Bloomberg reported at the end of February that a lawsuit alleging Facebook Inc. photo scanning technology flouts users’ privacy rights can proceed.
As TechCrunch summarised, when asked to clear a higher bar for privacy, Facebook has instead delved into design tricks to keep from losing our data.
Facebook needs to axe Face Recognition, or make it work in ways that are lawful, to face up to its responsibilities, and fast.
The Cambridge Analytica scandal has also brought personalised content targeting into the spotlight, but we are yet to see really constructive steps to row back to more straightfoward advertising, and away from todays’s highly invasive models of data collection and content micro-targeting designed to to grab your personalised attention.
Meanwhile policy makers and media are obsessed with screen time limits as a misplaced, over-simplified solution to complex problems, in young people using social media, which are more commonly likely to be exacerbating existing conditions and demonstrate correlations rather than cause.
Children are stuck in the middle.
Their rights to protection, privacy, reputation and participation must not become a political playground.